Curves
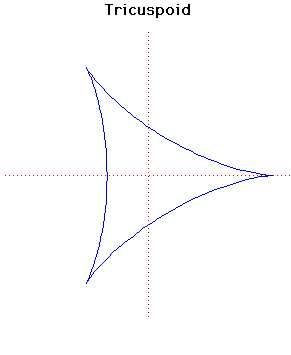
Tricuspoid
Description
The tricuspoid or deltoid was first considered by Euler in 1745 in connection with an optical problem. It was also investigated by Steiner in 1856 and is sometimes called Steiner's hypocycloid.The length of the tangent to the tricuspoid, measured between the two points in which it cuts the curve again is constant and equal to . If you draw tangents at and they are at right angles.
The length of the curve is and the area it encloses is .
In the parametric form the cusps occur at and . Notice the similarity between the parametric form of the tricuspoid and the parametric form of the cardioid.
The pedal of the tricuspoid, where the pedal point is the cusp, is a simple folium. The pedal, where the pedal point is the vertex, is a double folium. If the pedal point is on the inscribed equilateral triangle then the pedal is a trifolium.
The caustic of the tricuspoid, where the rays are parallel and in any direction, is an astroid.
Other Web site:
Xah Lee